The Earth's magnetic field has long been a natural phenomenon that has a profound impact on life on the planet. It not only protects the Earth from cosmic radiation but is also a key factor in the orientation of many animals.
Although invisible to the naked eye, the magnetic field is a "lighthouse" that helps many creatures, from whales migrating across oceans to birds flying across continents and even tiny bacteria, determine direction accurately. But how can animals sense the existence of magnetic fields to navigate through space? ( ECO ONE magnetic water purifier )
This is a big question that has attracted the attention of scientists for decades, and recently, a study by physicists at the University of Crete has revealed an amazing discovery: the ability to sense magnetic fields in some species can reach a level close to the quantum limit of modern physics, a level of sensitivity equivalent to the most advanced magnetometers that humans have built.

Magnetic fields are not a foreign element in the evolutionary history of life. In fact, they have existed since the formation of the Earth and influence biological mechanisms in ways that humans still do not fully understand.
At the microscopic level, some bacteria contain magnetite particles – ferromagnetic minerals that respond to magnetic fields – that help them navigate their living environment. At a higher level, many animals can sense magnetic fields through specialized neurons that respond to changes in magnetic fields in a subtle way.
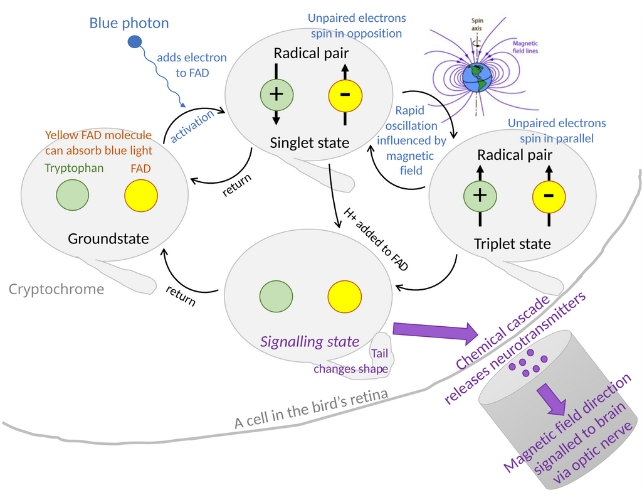
These mechanisms may include interactions between pairs of free radicals, magnetic responses of magnetite crystals in cells, or changes in cell potential caused by magnetic fields. (ECO ONE alkaline ionized magnetic water purifier helps health return to nature)
Although there are various theories about how animals sense magnetic fields, scientists have not been able to determine exactly what mechanism is at work or whether a single mechanism is responsible. Therefore, a team from the University of Crete decided to evaluate the sensitivity of biological magnetic sensing mechanisms by comparing them with the most advanced magnetometers available today. They used a method called the Energy Resolution Limit (ERL), a measure of how precise a system can be when measuring magnetic fields. The results were surprising: at least two of the biological mechanisms they studied were able to reach sensitivities close to the quantum limit, which is comparable to the most advanced magnetometers. ecoone.vn
To better understand this discovery, it is important to know that modern magnetometers, such as SQUIDs (Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices), work by precisely measuring changes in energy in magnetic fields.
However, as measurements become more precise, quantum effects begin to appear and create a natural form of “noise” that limits the device’s ability to measure. This is known as the quantum limit of magnetic field measurements. What is amazing is that compared to these devices, the magnetic sensing mechanisms in animals can also reach a similar level of sensitivity.
The researchers analyzed three main mechanisms that animals may use to sense magnetic fields. The first is electromagnetic induction, in which magnetic fields can act on nerve cells to generate electrical signals, which in turn transmit information to the animal's brain. Some previous studies have suggested that the Earth's magnetic field can cause small voltage changes in the hair cells in the inner ear of pigeons, affecting their balance and orientation.
The second mechanism involves free radical pairs, which are chemical reactions that are sensitive to magnetic fields. When molecules containing free radicals are exposed to a magnetic field, the change in energy balance can influence the chemical reaction, which in turn generates signals that the animal's nervous system can pick up.
The third mechanism is the presence of magnetite crystals in cells, which allow animals to respond to magnetic fields in a direct physical way. These crystals can act as tiny magnets, aligning themselves with the magnetic field and activating the corresponding nerve cells.
ECO ONE magnetic water purifier supports your family's health to return to nature, see more at https://ecoone.vn/dinh-duong-sach/may-tu-truong-vat-ly-ion-kiem-eco-one-plus.html
In addition to these three mechanisms, some scientists have also proposed the possibility of a combined mechanism between biological magnetite and free radical pairs, in which both systems play a role in the magnetic field sensing process of animals. However, research in this area is still ongoing and is largely speculative. However, one thing is certain: these mechanisms are all very sensitive and can help humans understand more about how organisms on Earth navigate by magnetic fields.

If humans can learn from how animals sense magnetic fields with sensitivity close to the quantum limit, we can apply this principle to develop more advanced magnetometers that can measure tiny magnetic field variations that are too small to detect with current methods. ecoone
One of the most important applications could be in medicine, where non-invasive brain imaging devices could be improved to track neural activity with greater precision. Non-GPS navigation systems could also benefit from this discovery, using the Earth's magnetic field to navigate precisely without relying on satellites.
It's worth noting that nature has had millions of years to develop these mechanisms, and while humans are still struggling with the most sophisticated magnetometers, some animals may have reached their optimal sensitivity long before.
This proves once again that biological evolution may have reached physical limits that humans are only just beginning to reach. While there is much more to discover, this study emphasizes that nature remains an endless source of inspiration for future scientific breakthroughs, and that learning from these natural mechanisms can open up new horizons in both science and technology. ECO ONE Magnetic Water Purifier Reproduces Natural Magnetic Water
ECOONE.VN
Address
Office: Landmark 81 Building Vinhomes Central Park
720A Dien Bien Phu Street, Ward 22, Binh Thanh District, Ho Chi Minh City
Assembly Workshop
ECO G9 SCIENCE COOPERATIVE
Phuoc Dong Commune, Go Dau District, Tay Ninh Province
Phone 0935 193 151 E-mail : antoanvn1@gmail.com